Table of Contents
Thresholds allow you to identify specific problems in your network quickly. When you set a threshold, you are defining what is considered to be normal traffic levels for a switch or interface. If that traffic level is exceeded, then the threshold fires, and is highlighted for further investigation or action.
Thresholds are configured and monitored on the Thresholds tab in sFlowTrend-Pro.
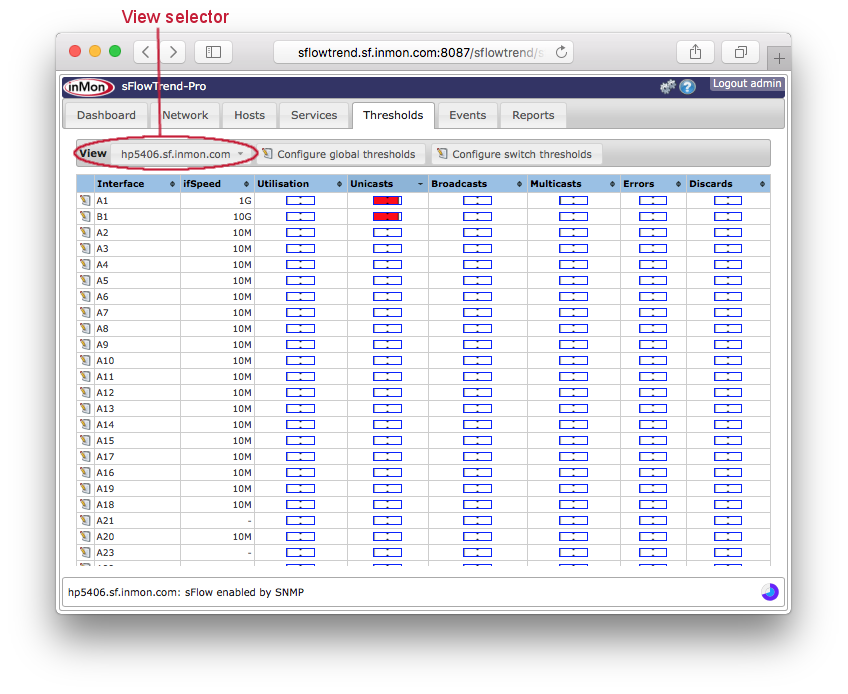
The Thresholds tab allows you to view the current status (from the previous minute) of different thresholds (see Section 7.1, “Viewing thresholds”). You can also drill-down to identify the root cause of a threshold violation (see Section 7.4, “Root cause analysis”) and to view the trend of the traffic levels.
You can view and configure the thresholds for all switches, or for all interfaces on a specific switch. Use the View selector to select the view that you would like. The options are:
- All Switches
- Displays a table of thresholds for each switch.
- All Interfaces
- Displays a table of thresholds for every interface on each switch.
- Customized thresholds
-
Displays only the thresholds for switches or
interfaces that have been customized (see
Section 7.3, “Defining thresholds
 ”).
”).
- Switch name or address
- If you select a specific switch (by name or IP address, depending on the switch naming policy configured in → ), the thresholds for each interface on that switch are displayed.
The current threshold values are shown in the table. Each column can be sorted by clicking on the header column. If you click on a column containing thresholds, then the column will be sorted by the current threshold values in the column. This is an easy way to find the thresholds with the highest values (ie, those that have 'most exceeded' the configured thresholds).